Understanding the Impact of Heartburn
Heartburn, often dismissed as a minor inconvenience, is a widespread condition that affects millions of people globally. It is characterized by a burning sensation in the chest after eating, often after eating, lying down, or bending over. While occasional heartburn might result from overindulgence in food or beverages, frequent or persistent episodes of heartburn could signal an underlying medical issue, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). GERD is a chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, leading to inflammation and, in severe cases, complications like esophageal ulcers or Barrett’s esophagus.
The Importance of Managing Heartburn
Understanding heartburn is crucial for its effective management. Its causes are multifactorial, ranging from lifestyle choices and dietary habits to anatomical and physiological abnormalities. Furthermore, untreated heartburn and quality of life not only diminishes quality of life but can also pose long-term health risks. This article delves into the root causes of heartburn and acid reflux, discusses the latest research findings, and explores the available treatments, offering a comprehensive guide to managing this common yet disruptive condition.
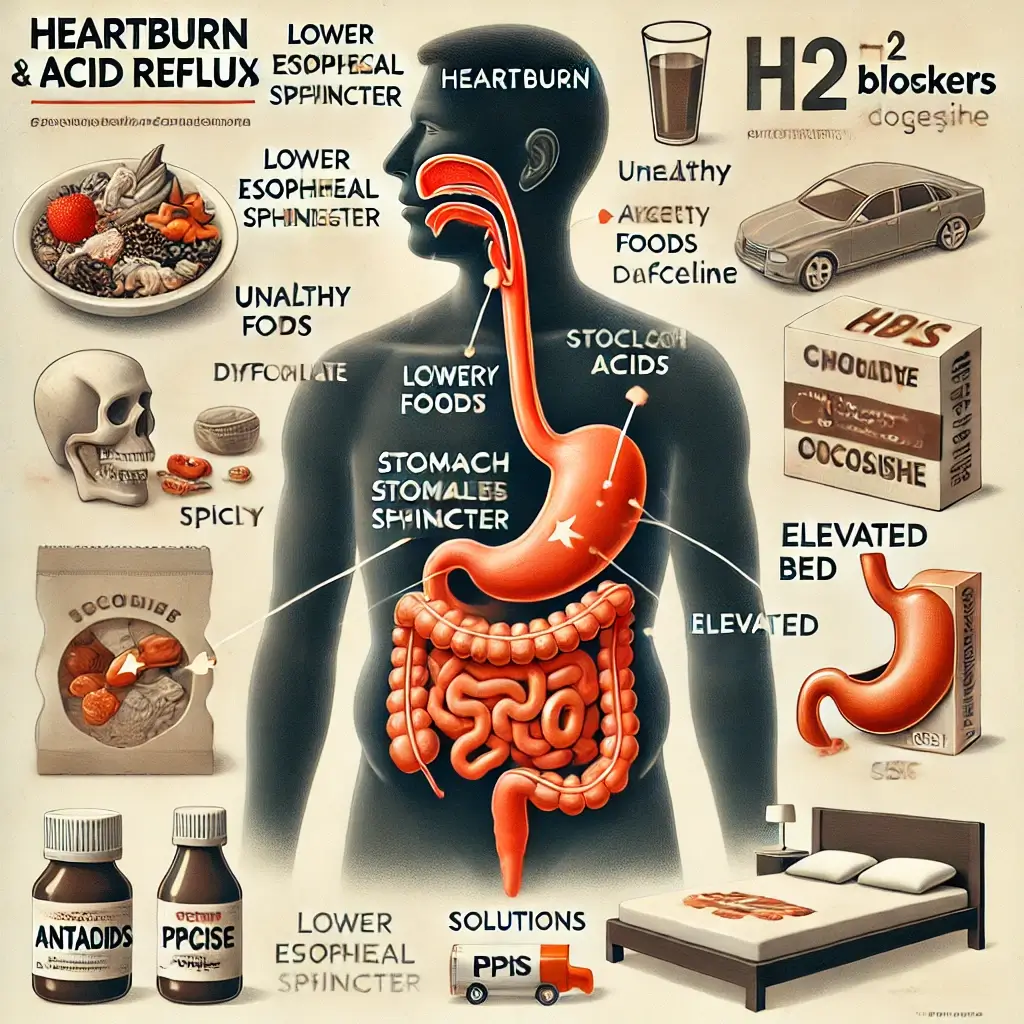
Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) Dysfunction
The LES, a muscular valve between the esophagus and stomach, is the primary barrier preventing stomach acid from traveling upward. In individuals with heartburn or acid reflux, the LES often weakens or relaxes inappropriately, allowing acidic stomach contents to irritate the esophagus. Research Findings: A 2006 study by Vakil et al. demonstrated that obesity and hiatal hernia complications, and specific dietary triggers are significant contributors to LES dysfunction. Obesity, in particular, exerts pressure on the abdomen, weakening the LES over time.
Dietary and Lifestyle Impact on Heartburn
Certain foods and drinks, such as spicy foods causing acid reflux, fatty meals, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol, are known to relax the LES. Smoking exacerbates the condition by impairing the sphincter’s functionality. Global Trends: A 2018 report emphasized lifestyle changes as the cornerstone for managing mild heartburn. Reducing intake of known triggers and maintaining a healthy weight have proven to be effective strategies for many individuals.
Pregnancy-Related Acid Reflux
Pregnancy and hormonal changes in acid reflux increases the risk of acid reflux due to hormonal changes that relax the LES and increased abdominal pressure from the growing uterus. While heartburn often resolves postpartum, proper management during pregnancy is essential to ensure maternal comfort and health.
Effective Management Strategies
Simple adjustments can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of heartburn episodes: Avoid Trigger Foods: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is often the first step. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Weight loss reduces abdominal pressure, alleviating LES dysfunction. Sleep Adjustments: elevating the head of bed for acid reflux reduces nighttime reflux symptoms by preventing stomach acid from traveling upward.
Medication Options for Relief
OTC antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) offer quick and effective symptom relief: Antacids neutralize stomach acid, providing immediate relief. H2 blockers and PPIs reduce acid production, addressing the root cause. For severe or persistent symptoms, prescription medications for chronic heartburn may be required. These include stronger doses of H2 blockers and PPIs, as well as prokinetic agents that improve stomach emptying.
Clinical Evidence and Surgical Solutions
Clinical Evidence: Fass et al. (2018) highlighted the efficacy of long-term PPI use for esophageal damage in preventing esophageal damage while noting potential side effects, such as nutrient malabsorption and increased infection risk. In rare cases, surgery may be necessary. Procedures such as fundoplication, where the top of the stomach is wrapped around the LES to strengthen it, are effective for patients with medication-resistant GERD. Emerging therapies like magnetic sphincter augmentation are also gaining attention.
Latest Research Developments
Recent studies explore the connection between gut microbiota imbalances and acid reflux symptoms. Preliminary findings suggest that probiotics could play a role in managing symptoms by improving overall gut health. Plant-based diets, which reduce the intake of acid-producing foods, have shown promise in managing heartburn symptoms. Alkaline water is another alternative being explored for its potential to neutralize stomach acid.
Public Health Initiatives
Countries worldwide are launching campaigns to educate individuals about heartburn prevention through lifestyle changes. For instance, Europe’s “Stop Acid Burn” initiative promotes early intervention strategies for GERD and public awareness about GERD.
Final Thoughts on Heartburn Management
Heartburn and acid reflux, though common, can be debilitating if left unaddressed. By understanding the root causes, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage symptoms. lifestyle modifications for preventing acid reflux remain the foundation of treatment, supported by OTC or prescription medications when necessary. For severe cases, surgical interventions provide a viable solution. Additionally, emerging research offers hope for novel therapies and prevention strategies.
Importance of Medical Intervention
Ultimately, addressing heartburn is about more than just alleviating discomfort—it’s about improving quality of life and preventing long-term complications. If symptoms persist despite interventions, seeking medical advice for chronic heartburn is crucial for a tailored treatment plan.