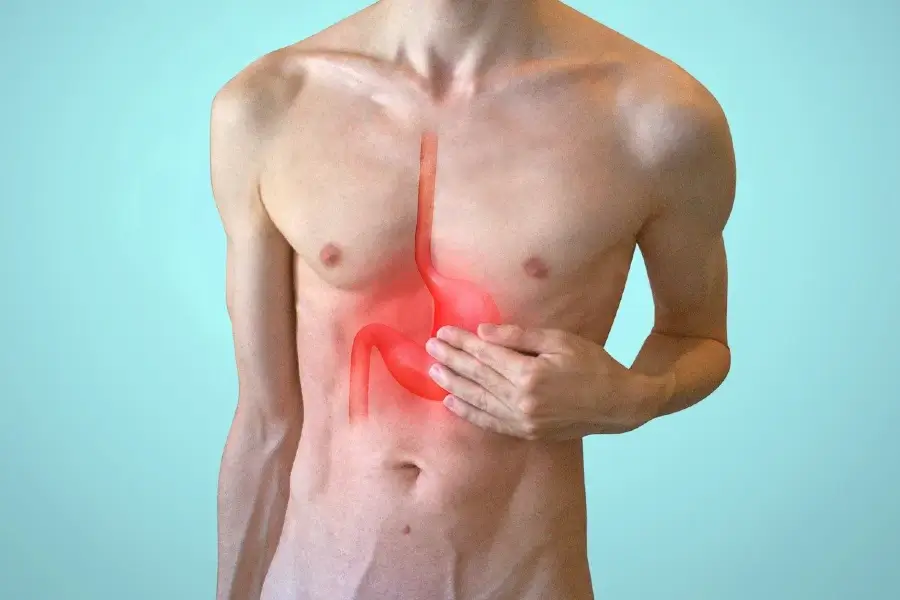
Heartburn is characterized by a burning discomfort that can go on for anywhere from a few minutes to several hours and is most frequently experienced in the chest section. The esophagus is the tube that transports food and fluids from the mouth into the stomach. This condition happens when the stomach contents flood back into the esophagus. A circular muscle known as the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is the point at which the esophagus and the stomach fuse.
This occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) relaxes too frequently or does not function properly, permitting stomach contents to wash up into the esophagus. Prolonged exposure to stomach acids can damage the lining of the esophagus over time, resulting in precancerous alterations or even more advanced esophageal cancer.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole (Prilosec) and pantoprazole (Protonix), decrease the amount of acid produced by the stomach.
Over-the-counter antacids or more potent prescription drugs, such as proton pump inhibitors and H2 blockers, are typically effective treatments for people who have heartburn on an occasional or minor basis. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole (Prilosec) and pantoprazole (Protonix), decrease the amount of acid produced by the stomach.
It is true that weaker medications, such as antacids, can lessen the quantity of acid that can enter the esophagus; however, these medications do not solve the underlying issue that is causing the acid to flow into the esophagus in the first place.
You should schedule an appointment with your physician to evaluate your heartburn and discuss possible treatment options if you experience severe or frequent heartburn. Your physician will question you regarding the symptoms you are experiencing and the frequency with which they occur. Additionally, your physician will conduct tests to evaluate your esophagus and measure the amounts of acid in your body.
Avoid lying down or bending over as soon as possible; both of these motions might cause the stomach to create excessive acid.
Your physician may recommend alterations to your lifestyle and food to either avoid or alleviate heartburn. In addition, you should avoid going to bed with a full stomach (allow three to five hours between your previous meal and lying down), eat smaller meals, and avoid foods that cause heartburn.
When you have finished eating, you should avoid lying down or bending over as soon as possible. Both of these motions might cause the stomach to create excessive acid. Additionally, if you want to reduce weight, you should make an effort to abstain from drinking alcoholic or carbonated beverages.
These include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and acetaminophen (Tylenol), both of which are prevalent over-the-counter and prescription medications that might make heartburn worse. It would help to avoid or take them with food to reduce irritation.
If the modifications you make to your diet and lifestyle do not manage your heartburn well, your doctor may suggest a procedure to alleviate acid reflux.
Narcotic pain relievers like oxycodone and hydrocodone, as well as antidepressants like citalopram (Celexa) and fluoxetine (Prozac), are examples of additional drugs that have the potential to act as irritants to the esophagus.
If the modifications you make to your diet and lifestyle do not manage your heartburn well, your doctor may suggest a procedure to alleviate acid reflux. To remove acid reflux and prevent long-term damage to the esophagus, esophageal specialists at UCI Health can provide minimally invasive operations that do not require incisions.