There is still potential for improvement in the detection and treatment of stomach cancer, even though significant progress has been made in this area. The following is a breakdown of the current landscape as well as areas of development that indicate promise:
Diagnostic Methods That Have Been Improved:
A timely diagnosis is essential for effective therapy; early detection is also crucial. More sophisticated and easily accessible diagnostic procedures are being developed, such as upper endoscopy with biopsy and stool tests for occult blood.
Imaging techniques like computed tomography (CT) scans, positron emission tomography (PET) scans, and endoscopic ultrasonography are increasingly sophisticated. This enables them to improve tumor characterization, staging, and treatment planning.
Biomarkers: Finding specific biomarkers in blood or tissue samples is a promising area of research that offers the potential to detect stomach cancer earlier and without invasive procedures.
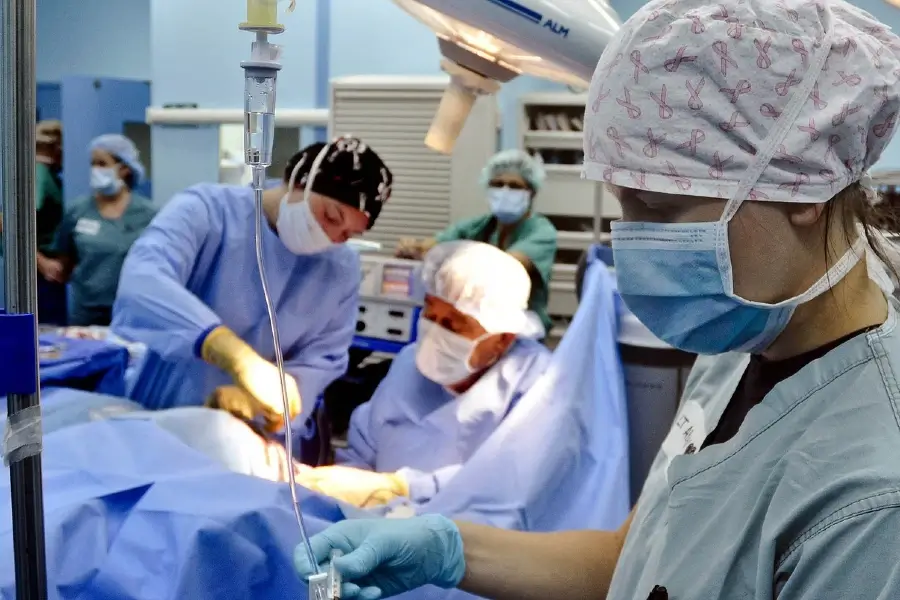
Minimally invasive surgery, such as laparoscopic and robotic procedures.
Recent Developments in Treatment:
Minimally invasive surgery, such as laparoscopic and robotic procedures, is becoming increasingly used for the treatment of stomach cancer. These procedures provide shorter recovery times and the possibility of reduced pain.
The development of personalized therapies, which are targeted medicines based on the tumor’s exact genetic makeup, is allowing for a more precise range of therapeutic choices.
Combination therapies: The traditional method, which has led to increased survival rates, is to combine surgery with treatments like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy medications, which assist the immune system in killing cancer cells, are receiving a lot of positive feedback as a potential therapeutic option for some intestinal cancer patients.
In recent years, oncology has witnessed remarkable developments.
Potentially Fruitful Research Domains:
Early detection and risk stratification: Identifying individuals at high risk and creating noninvasive screening technologies for early detection are both essential research areas.
Minimally invasive treatment options: Research and development are ongoing to further optimize minimally invasive surgical procedures and ablation therapies for treating localized cancers.
In recent years, oncology has witnessed remarkable developments, with a special focus on developing targeted medicines. These advancements have been made possible by the development of advanced targeted therapies.
These innovative treatments aim to address the underlying genetic and molecular drivers of cancer, giving a more tailored and practical approach in comparison to conventional chemotherapies that cover a broad range of cancers.
A significant section of research in this field involves the creation of more sophisticated targeted medicines.
A significant section of research in this field involves the creation of more sophisticated targeted medicines. Researchers are now investigating genetic abnormalities and signaling pathways essential for the growth and survival of different types of cancer cells to find and comprehend these specific mutations and pathways.
By focusing on these specific molecular fingerprints, researchers can develop treatments that selectively and efficiently kill cancerous cells while causing the least damage to healthy organs.
This technique has several attractive features compared to more traditional therapies. First, these medicines have the potential to be more effective in treating and possibly even eradicating the disease than other treatments since they focus on the specific characteristics of a tumor.
The second advantage is that they tend to have a more favorable side-effect profile. This is because they are designed to spare healthy cells and lessen the systemic toxicity inherent in conventional chemotherapy treatments.
A multi-step procedure is required to produce enhanced targeted medicines. This method combines cutting-edge genomic research with sophisticated drug design and rigorous clinical testing.
Researchers are employing cutting-edge molecular profiling tools, such as next-generation sequencing, to decipher the intricate genetic landscape of various malignancies. This information is then utilized to locate innovative therapeutic targets and direct the development of highly specific and powerful drug candidates.
Assist researchers in simulating the interactions between potential medications and their molecular targets.
In addition, rapidly developing technology, like artificial intelligence and machine learning, has further expedited the rate at which tailored medicines are discovered and optimized.
These technologies can assist researchers in simulating the interactions between potential medications and their molecular targets, facilitating the quick screening and refining of possible drug candidates.
As the field of sophisticated targeted therapies continues to develop, oncologists and researchers maintain a positive outlook regarding the potential of these tailored techniques to revolutionize how we manage and treat different types of cancer.
The future promises cancer treatments that are more effective, less toxic, and transformative. Harnessing the power of precision medicine can realize this promise.
The optimization of treatment combinations: Research is currently being conducted to optimize the combinations of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy for various stages and forms of stomach cancer.
It appears that the prognosis for stomach cancer is improving overall. Early detection, minimally invasive therapies, and tailored approaches are achieving more effective outcomes. Nevertheless, research is necessary to further improve the diagnostic process, the effectiveness of treatment, and overall survival rates.